ERACLIM 2
Mitarbeiter:
- L. Haimberger
- M. Blaschek
- M. Mayer
--> weiter zur Projekt-Seite des Fördergebers
The core objective of the EU-FP7 ERA-CLIM2 project (Buizza et al, 2018, BAMS, in press) was to apply and extend current global reanalysis capability in Europe, to meet the challenging requirements for climate monitoring, climate research, and the development of climate services.
ERA-CLIM2 was a 4-year project that started in January 2014 and that exploited the strengthens and consolidated the work begun in the EU-FP7 ERA-CLIM project, which ended December 2013. ERA-CLIM2, which ended in December 2017, expanded considerably the scope of its predecessor project and many aspects.
ERA-CLIM2 has contributed to advancing reanalysis science and development in four main areas:
- Observation data rescue and post-processing: activities under this theme include a large effort on data rescue for historic in-situ weather observations around the world, and substantial work on the reprocessing of satellite climate data records and enabling the use of historical satellite data for reanalysis;
- Data assimilation methods: activities under this theme aim to progress the development and testing of ‘coupled assimilation methods’, capable of including observations from different Earth-system components (land surface, ocean, sea-ice, atmosphere, chemical components, …) to produce a more consistent estimate of the Earth-system evolution, especially at the surface;
- Reanalysis production: activities under this theme aim to generate the innovative reanalysis data-sets, such as the first European coupled ocean-land-atmosphere reanalysis of the 20th century, and to provide access to the reanalysis data;
- Evaluation and uncertainty estimation: activities under this theme aim to assess the reanalyses’ quality and how products differ from previous uncoupled products, and to develop methods for estimating uncertainty in reanalyses.
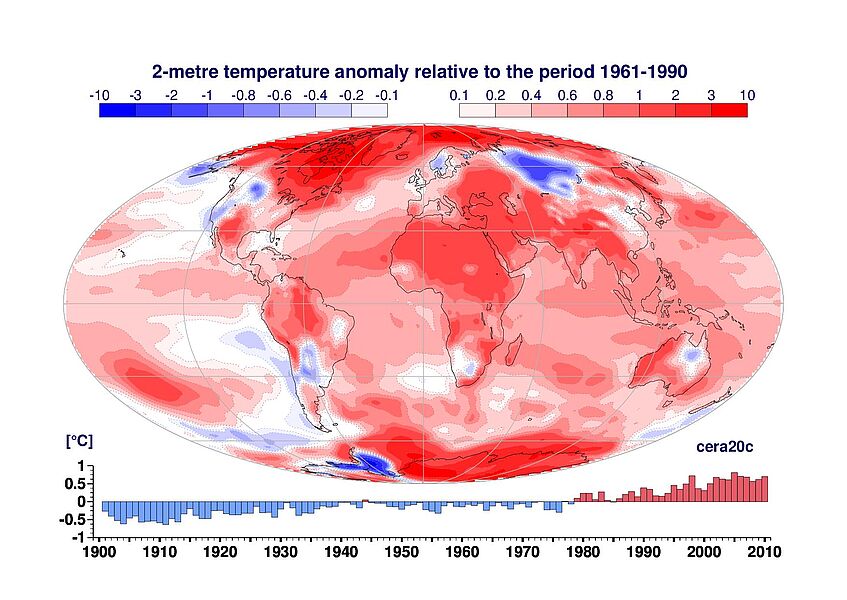
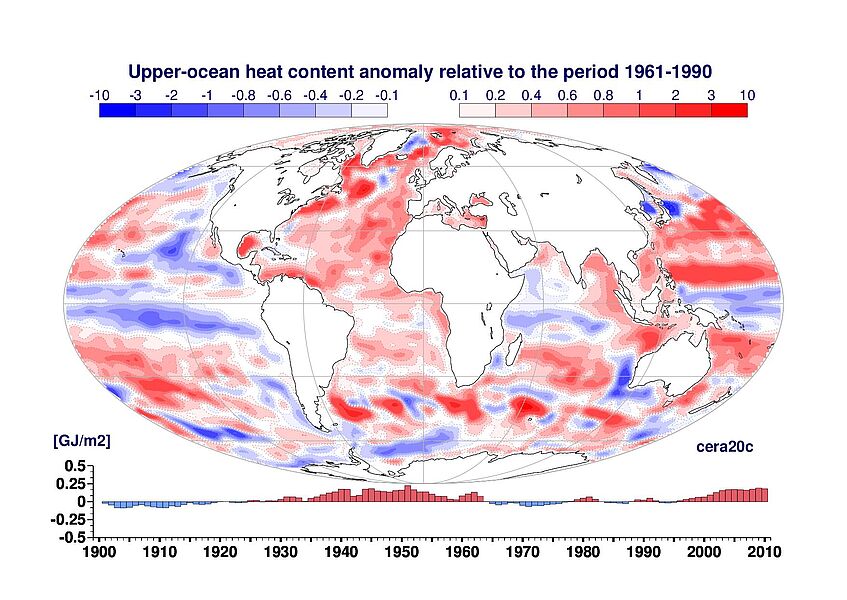
The two figures below give an example of the ERA-CLIM2 deliverables. The two maps show the annual-average 2-meter temperature anomaly (top) and the upper-ocean heat content anomaly (bottom), computed with respect to the 1961-1990 average. The two bar diagrams with the time series, show the evolution of yearly global-mean anomalies relative to the period 1961–1990 for two-metre temperature (top) and upper-ocean heat content (bottom). These figures have been computed from the CERA-20C reanalysis, the first European coupled ocean, land and atmosphere reanalysis that covers the 20th century (from 1901 to 2010).